Jenkins Tutorial for Beginners: Mastering CI/CD with Docker
Jenkins Tutorial for Beginners: Mastering CI/CD with Docker
Nov 13, 2024
Jithin
Nov 13, 2024


Jithin





Jenkins Tutorial for Beginners: Mastering CI/CD with Docker in DevOps
If you're a beginner looking to understand Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) workflows, this Jenkins Tutorial for Beginners is your perfect guide. Jenkins, a widely-used open-source automation tool, paired with Docker, a containerization platform, simplifies software delivery pipelines. Together, they create a seamless CI/CD environment, making development, testing, and deployment faster and more efficient.
In this practical guide, we will break down Jenkins and Docker, their integration for a smoother CI/CD pipeline, and how they simplify deployments, reduce errors, and save time. Whether you're eyeing Jenkins for DevOps or curious about Jenkins on AWS, you are about to discover a skill that will boost your career and give you a competitive edge.

Source: Image
What is Jenkins?
Jenkins is an open-source tool written in Java, designed to automate tasks such as building, testing, and deploying applications. Its flexibility, supported by a vast plugin ecosystem, makes it an indispensable tool for DevOps teams.
Why Beginners Should Learn Jenkins:
Jenkins is beginner-friendly, especially because it’s free and widely documented. If you’re new to software development or DevOps, Jenkins can help you:
Automate repetitive tasks like building and testing code.
Learn about CI/CD pipelines, which are crucial in modern software development.
Get hands-on experience with a tool that’s used in companies worldwide.
Key Benefits of Jenkins for DevOps Teams
Open-source and Free: Cost-effectiveness without sacrificing capability.
Flexible Plugin Ecosystem: Jenkins offers over 1,800 plugins, allowing customization and seamless integration with other tools.
Continuous Integration & Continuous Deployment: Automates testing, building, and deploying, ideal for fast-paced development cycles.
By automating these processes, Jenkins cuts down deployment time and minimizes human error. Picture it as your tech co-pilot, ensuring everything works as intended before release.
What is Docker?
Docker is a tool that packages your application and its dependencies into a container. Containers ensure your application works the same way, whether on your computer or a server.
Why Use Docker in CI/CD?
Docker allows applications to run consistently across various environments, which is key to DevOps. Docker packages an application and its dependencies into a container, creating a consistent environment that can run on any system with Docker installed.
Benefits of Docker in Jenkins CI/CD Pipelines
Docker ensures consistent environments across development, testing, and production by packaging applications into containers. Integrating Docker with Jenkins enhances the CI/CD pipeline by ensuring reliable builds and deployments.
Environment Consistency: Avoids the “works on my machine” issue.
Scalability: Easily deploys multiple instances, helpful for high-traffic apps.
Efficient Resource Management: Lightweight containers use fewer resources than virtual machines, optimizing performance.
Combining Jenkins and Docker enhances CI/CD efficiency, ensuring that the same code runs seamlessly on multiple platforms.
Setting Up Jenkins with Docker: A Step-by-Step Guide
Are you ready to dive in? Here’s a practical walk-through for setting up Jenkins and Docker, including setup tips for beginners.
Step 1: Install Docker
Download Docker from the official website and follow installation instructions.
Verify installation by running docker --version.
Pro Tip: Docker installation may vary based on OS, so refer to Docker’s installation guide.
Step 2: Install Jenkins in a Docker Container
Pull the official Jenkins Docker image:
bash
Copy code
docker pull jenkins/jenkinsStart the Jenkins container:
bash
Copy code
docker run -p 8080:8080 -p 50000:50000 jenkins/jenkinsAccess Jenkins at http://localhost:8080 in your browser.
This setup isolates Jenkins in a container, ensuring environment consistency and easier troubleshooting.
Step 3: Configure Jenkins for CI/CD
Install Plugins: Go to the Jenkins dashboard > Manage Jenkins > Manage Plugins.
Set Up a Jenkins Pipeline: Go to New Item > Pipeline, then configure as per your project requirements.
Using Jenkins with Docker containers lets you create reliable CI/CD pipelines that handle testing, building, and deployment processes automatically.
Building Your First CI/CD Pipeline with Jenkins and Docker
Creating your first CI/CD pipeline with Jenkins and Docker is an exciting way to automate the building, testing, and deployment of your application. Now, let’s create a basic CI/CD pipeline with Jenkins, using Docker as the containerization tool.
Prerequisites:
Before creating your CI/CD pipeline, you will need;
Jenkins Installed: Either on your local machine or a server (You can run Jenkins in a Docker container too).
Docker Installed: You will need Docker installed to build and run containers.
Git Repository: The codebase you want to integrate with Jenkins (Usually a GitHub or GitLab repository).
A Dockerfile: A Dockerfile to containerize your application (This is crucial if you want to deploy your application in Docker).
Example Pipeline Code
Here’s a simple Jenkins pipeline script for a Node.js application in Docker:

What Does This Script Do?
Build: Installs dependencies using npm.
Test: Runs tests to ensure the code is error-free.
Deploy: Starts the application for deployment.
This CI/CD pipeline automates the entire process, freeing up time for you to focus on new features and improvements.
Tips for Beginners
Start Small: Focus on learning basic features before diving into advanced configurations.
Use the Community: Explore Jenkins documentation and forums for help.
Experiment: Try creating simple pipelines for personal projects to understand how things work.
Keep Things Updated: Regularly update Jenkins and its plugins for security and performance.
Jenkins on AWS: Streamlining Cloud Deployment
For those leveraging cloud infrastructure, Jenkins on AWS is a game-changer. Running Jenkins on Amazon Web Services (AWS) allows for scalable, reliable CI/CD, especially for larger projects.
Why Use Jenkins on AWS?
For those looking to scale up, running Jenkins on AWS offers additional benefits:
Flexibility: AWS provides resources for large-scale deployments.
Reliability: Jenkins on AWS handles heavy workloads efficiently.
Setting Up Jenkins on AWS
Launch an EC2 Instance: Choose an instance (t2.micro works for small projects).
Install Docker and Jenkins: Follow the Docker and Jenkins installation steps as above.
Configure Jenkins with S3 and ECS: Use Jenkins plugins to integrate with Amazon S3 and ECS for smoother CI/CD.
AWS integration enables Jenkins to manage applications at scale, from microservices to enterprise-level deployments, adding flexibility and resilience to the CI/CD pipeline.
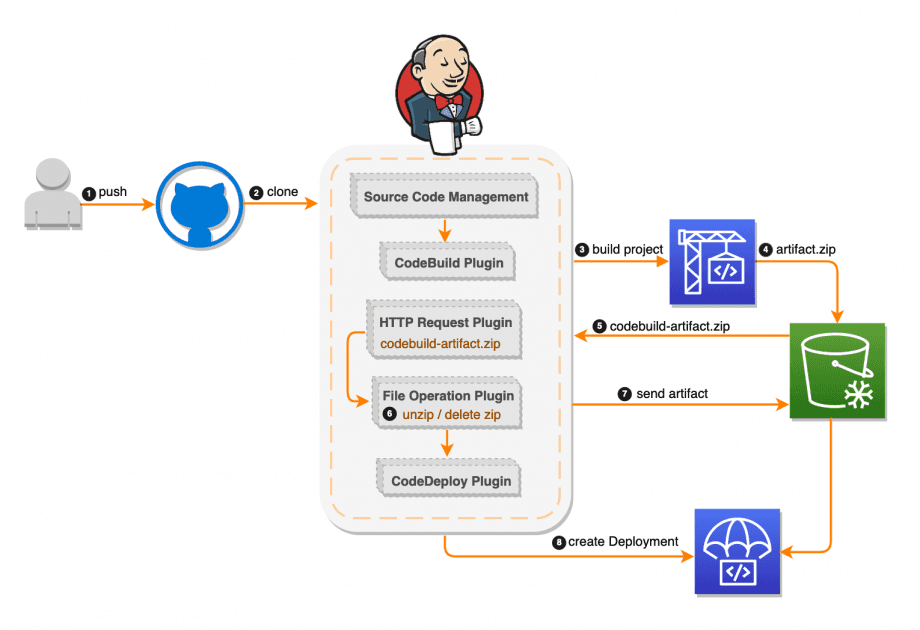
Source: Image
Common Jenkins Tools to Enhance CI/CD Pipelines
Jenkins offers various plugins and integrations for DevOps:
GitHub Integration: Integrates Jenkins with GitHub for automated pull requests and branch management.
Jenkins Blue Ocean: An intuitive UI for building and visualizing pipelines.
Docker Pipeline Plugin: Allows Jenkins to build and publish Docker images.
AWS CodePipeline Plugin: Integrates Jenkins with AWS CodePipeline, a managed CI/CD service.
Each tool enhances Jenkins’ functionality, making it a more versatile choice for developers and DevOps teams.
Best Practices for Jenkins and Docker in CI/CD
Integrating Jenkins and Docker into your CI/CD pipeline is a powerful way to ensure consistency, speed, and scalability in your software development cycle. To get the most out of Jenkins and Docker in CI/CD, consider these best practices:
Keep Pipelines Short and Simple: Long, complex pipelines increase build time and the risk of errors.
Use Version Control: Always version-control your Jenkins pipeline scripts.
Monitor Pipeline Performance: Use tools like Prometheus or Grafana to monitor pipeline performance and optimize accordingly.
Regularly Update Plugins: Outdated plugins can create security risks and reduce efficiency.
Following these tips will help maintain an optimized CI/CD pipeline, making deployments smoother and reducing bottlenecks.
Conclusion: Ready to Master CI/CD?
This Jenkins Tutorial for Beginners has introduced you to Jenkins, Docker, and the essentials of CI/CD pipelines. By mastering Jenkins and Docker, you can automate software delivery, minimize errors, and boost productivity.
Are you ready to take the next step in your DevOps journey? At Skillect, we are committed to making tech education accessible and hands-on. Dive deeper into CI/CD, Jenkins, and Docker with Skillect’s comprehensive courses designed for aspiring DevOps professionals. We believe in practical learning that converts skills into career opportunities.
Now, do you want to level up your DevOps skills? Join Skillect today and become a CI/CD pro!
Jenkins Tutorial for Beginners: Mastering CI/CD with Docker in DevOps
If you're a beginner looking to understand Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) workflows, this Jenkins Tutorial for Beginners is your perfect guide. Jenkins, a widely-used open-source automation tool, paired with Docker, a containerization platform, simplifies software delivery pipelines. Together, they create a seamless CI/CD environment, making development, testing, and deployment faster and more efficient.
In this practical guide, we will break down Jenkins and Docker, their integration for a smoother CI/CD pipeline, and how they simplify deployments, reduce errors, and save time. Whether you're eyeing Jenkins for DevOps or curious about Jenkins on AWS, you are about to discover a skill that will boost your career and give you a competitive edge.

Source: Image
What is Jenkins?
Jenkins is an open-source tool written in Java, designed to automate tasks such as building, testing, and deploying applications. Its flexibility, supported by a vast plugin ecosystem, makes it an indispensable tool for DevOps teams.
Why Beginners Should Learn Jenkins:
Jenkins is beginner-friendly, especially because it’s free and widely documented. If you’re new to software development or DevOps, Jenkins can help you:
Automate repetitive tasks like building and testing code.
Learn about CI/CD pipelines, which are crucial in modern software development.
Get hands-on experience with a tool that’s used in companies worldwide.
Key Benefits of Jenkins for DevOps Teams
Open-source and Free: Cost-effectiveness without sacrificing capability.
Flexible Plugin Ecosystem: Jenkins offers over 1,800 plugins, allowing customization and seamless integration with other tools.
Continuous Integration & Continuous Deployment: Automates testing, building, and deploying, ideal for fast-paced development cycles.
By automating these processes, Jenkins cuts down deployment time and minimizes human error. Picture it as your tech co-pilot, ensuring everything works as intended before release.
What is Docker?
Docker is a tool that packages your application and its dependencies into a container. Containers ensure your application works the same way, whether on your computer or a server.
Why Use Docker in CI/CD?
Docker allows applications to run consistently across various environments, which is key to DevOps. Docker packages an application and its dependencies into a container, creating a consistent environment that can run on any system with Docker installed.
Benefits of Docker in Jenkins CI/CD Pipelines
Docker ensures consistent environments across development, testing, and production by packaging applications into containers. Integrating Docker with Jenkins enhances the CI/CD pipeline by ensuring reliable builds and deployments.
Environment Consistency: Avoids the “works on my machine” issue.
Scalability: Easily deploys multiple instances, helpful for high-traffic apps.
Efficient Resource Management: Lightweight containers use fewer resources than virtual machines, optimizing performance.
Combining Jenkins and Docker enhances CI/CD efficiency, ensuring that the same code runs seamlessly on multiple platforms.
Setting Up Jenkins with Docker: A Step-by-Step Guide
Are you ready to dive in? Here’s a practical walk-through for setting up Jenkins and Docker, including setup tips for beginners.
Step 1: Install Docker
Download Docker from the official website and follow installation instructions.
Verify installation by running docker --version.
Pro Tip: Docker installation may vary based on OS, so refer to Docker’s installation guide.
Step 2: Install Jenkins in a Docker Container
Pull the official Jenkins Docker image:
bash
Copy code
docker pull jenkins/jenkinsStart the Jenkins container:
bash
Copy code
docker run -p 8080:8080 -p 50000:50000 jenkins/jenkinsAccess Jenkins at http://localhost:8080 in your browser.
This setup isolates Jenkins in a container, ensuring environment consistency and easier troubleshooting.
Step 3: Configure Jenkins for CI/CD
Install Plugins: Go to the Jenkins dashboard > Manage Jenkins > Manage Plugins.
Set Up a Jenkins Pipeline: Go to New Item > Pipeline, then configure as per your project requirements.
Using Jenkins with Docker containers lets you create reliable CI/CD pipelines that handle testing, building, and deployment processes automatically.
Building Your First CI/CD Pipeline with Jenkins and Docker
Creating your first CI/CD pipeline with Jenkins and Docker is an exciting way to automate the building, testing, and deployment of your application. Now, let’s create a basic CI/CD pipeline with Jenkins, using Docker as the containerization tool.
Prerequisites:
Before creating your CI/CD pipeline, you will need;
Jenkins Installed: Either on your local machine or a server (You can run Jenkins in a Docker container too).
Docker Installed: You will need Docker installed to build and run containers.
Git Repository: The codebase you want to integrate with Jenkins (Usually a GitHub or GitLab repository).
A Dockerfile: A Dockerfile to containerize your application (This is crucial if you want to deploy your application in Docker).
Example Pipeline Code
Here’s a simple Jenkins pipeline script for a Node.js application in Docker:

What Does This Script Do?
Build: Installs dependencies using npm.
Test: Runs tests to ensure the code is error-free.
Deploy: Starts the application for deployment.
This CI/CD pipeline automates the entire process, freeing up time for you to focus on new features and improvements.
Tips for Beginners
Start Small: Focus on learning basic features before diving into advanced configurations.
Use the Community: Explore Jenkins documentation and forums for help.
Experiment: Try creating simple pipelines for personal projects to understand how things work.
Keep Things Updated: Regularly update Jenkins and its plugins for security and performance.
Jenkins on AWS: Streamlining Cloud Deployment
For those leveraging cloud infrastructure, Jenkins on AWS is a game-changer. Running Jenkins on Amazon Web Services (AWS) allows for scalable, reliable CI/CD, especially for larger projects.
Why Use Jenkins on AWS?
For those looking to scale up, running Jenkins on AWS offers additional benefits:
Flexibility: AWS provides resources for large-scale deployments.
Reliability: Jenkins on AWS handles heavy workloads efficiently.
Setting Up Jenkins on AWS
Launch an EC2 Instance: Choose an instance (t2.micro works for small projects).
Install Docker and Jenkins: Follow the Docker and Jenkins installation steps as above.
Configure Jenkins with S3 and ECS: Use Jenkins plugins to integrate with Amazon S3 and ECS for smoother CI/CD.
AWS integration enables Jenkins to manage applications at scale, from microservices to enterprise-level deployments, adding flexibility and resilience to the CI/CD pipeline.

Source: Image
Common Jenkins Tools to Enhance CI/CD Pipelines
Jenkins offers various plugins and integrations for DevOps:
GitHub Integration: Integrates Jenkins with GitHub for automated pull requests and branch management.
Jenkins Blue Ocean: An intuitive UI for building and visualizing pipelines.
Docker Pipeline Plugin: Allows Jenkins to build and publish Docker images.
AWS CodePipeline Plugin: Integrates Jenkins with AWS CodePipeline, a managed CI/CD service.
Each tool enhances Jenkins’ functionality, making it a more versatile choice for developers and DevOps teams.
Best Practices for Jenkins and Docker in CI/CD
Integrating Jenkins and Docker into your CI/CD pipeline is a powerful way to ensure consistency, speed, and scalability in your software development cycle. To get the most out of Jenkins and Docker in CI/CD, consider these best practices:
Keep Pipelines Short and Simple: Long, complex pipelines increase build time and the risk of errors.
Use Version Control: Always version-control your Jenkins pipeline scripts.
Monitor Pipeline Performance: Use tools like Prometheus or Grafana to monitor pipeline performance and optimize accordingly.
Regularly Update Plugins: Outdated plugins can create security risks and reduce efficiency.
Following these tips will help maintain an optimized CI/CD pipeline, making deployments smoother and reducing bottlenecks.
Conclusion: Ready to Master CI/CD?
This Jenkins Tutorial for Beginners has introduced you to Jenkins, Docker, and the essentials of CI/CD pipelines. By mastering Jenkins and Docker, you can automate software delivery, minimize errors, and boost productivity.
Are you ready to take the next step in your DevOps journey? At Skillect, we are committed to making tech education accessible and hands-on. Dive deeper into CI/CD, Jenkins, and Docker with Skillect’s comprehensive courses designed for aspiring DevOps professionals. We believe in practical learning that converts skills into career opportunities.
Now, do you want to level up your DevOps skills? Join Skillect today and become a CI/CD pro!
