Kubernetes Beginner Guide: A Comparison of AWS EKS, Azure AKS, and Google GKE
Kubernetes Beginner Guide: A Comparison of AWS EKS, Azure AKS, and Google GKE
Nov 8, 2024
Jithin
Nov 8, 2024


Jithin





Kubernetes Beginner Guide: Comparing AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Solutions
For beginners looking to understand Kubernetes, this Kubernetes Beginner Guide provides an easy-to-follow introduction and a comprehensive comparison of how Kubernetes works across major platforms: AWS Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), and Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). Kubernetes is revolutionizing cloud computing by simplifying application deployment and scaling, and this guide is your roadmap to getting started.
Kubernetes isn’t just a buzzword—it's the backbone of modern app deployment in the cloud. Let’s say you are a DevOps engineer, a tech enthusiast, or simply someone keeping up with cloud trends. You have likely encountered Kubernetes, and for good reason. This open-source platform, originally developed by Google, has transformed how we manage containerized applications. Today, every major cloud provider, from AWS, Azure, to Google Cloud, offers a unique way to leverage Kubernetes.
Imagine Kubernetes as the 'orchestra conductor' for your applications, managing and coordinating their deployment, scalability, and maintenance. But how does it work on the big cloud platforms? And what are the core differences among AWS Kubernetes, Azure Kubernetes, and Google Kubernetes? By the end of this guide, you will not only understand these distinctions but feel confident navigating them.
What is Kubernetes?
To understand how each cloud provider manages Kubernetes, let’s start with the basics. Kubernetes is an open-source platform designed for automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. Think of it as an ecosystem where your applications can run in isolated, lightweight containers that make deployment easier and more resilient.
Kubernetes architecture revolves around a master-slave setup, with a control plane (the 'brain') and worker nodes (the 'muscles') that do the heavy lifting. This separation ensures that applications are both stable and scalable, adjusting automatically based on the demand.
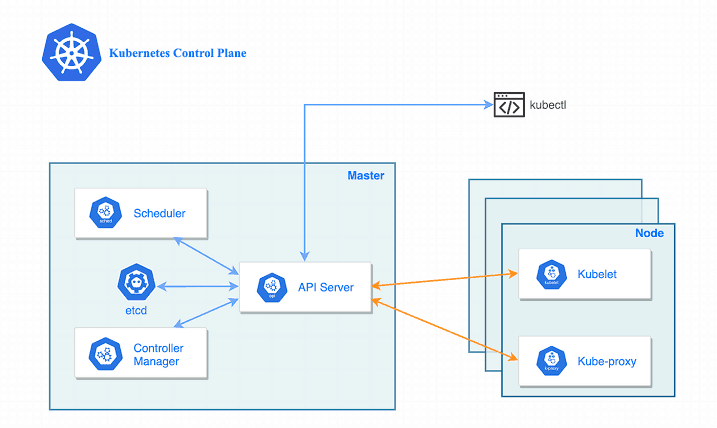
Source: Image
Key Features:
Automated Rollouts: Kubernetes can automatically roll out changes without downtime.
Self-Healing: It detects failed containers and replaces them.
Service Discovery: Exposes services and their IPs to other applications.
Why Start with Kubernetes?
As cloud-native technologies dominate the tech landscape, Kubernetes has become an essential skill for developers, DevOps engineers, and IT professionals.
According to recent reports, Kubernetes usage is projected to grow by over 20% annually due to its flexibility, scalability, and support for hybrid and multi-cloud setups make it a cornerstone for modern application management. Starting with Kubernetes gives you a head start in mastering cloud computing essentials.
This guide simplifies Kubernetes concepts and focuses on comparing its deployment on AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud to help you make an informed decision.
Kubernetes on AWS: Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)
Overview of AWS Kubernetes
AWS offers the Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), an easy-to-use, fully managed service. AWS Kubernetes emphasizes scalability and integrates deeply with AWS ecosystem tools, like IAM, ELB, and CloudWatch, providing seamless authentication, monitoring, and logging.
AWS Kubernetes Architecture
The architecture on AWS typically comprises EKS clusters where each cluster holds a control plane that communicates with worker nodes. AWS handles the heavy lifting on the control plane, while users only manage the worker nodes. This split of duties makes AWS Kubernetes architecture an excellent choice for teams with limited Kubernetes experience.
Pros and Cons of EKS:
Pros:
Full integration with AWS services
Scalable and high availability
Cons:
Can be complex for beginners
Pricing can add up quickly
Who Should Use AWS Kubernetes?
AWS Kubernetes is an excellent fit for teams already invested in the AWS ecosystem or those requiring high availability and advanced scaling options.
Kubernetes on Azure: Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
Overview of Azure Kubernetes
Azure brings its Kubernetes service, known as Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), offering deep integration with its DevOps tools like Azure DevOps, GitHub Actions, and Visual Studio Code.
Azure Kubernetes Architecture
In Azure, the Kubernetes control plane and the worker nodes are separated, much like in AWS. However, Azure further simplifies deployment with automation and monitoring tools that are already popular among enterprise users. This makes AKS a preferred choice for companies running multiple applications in hybrid cloud environments.
Pros and Cons of AKS:
Pros:
Seamless integration with Microsoft tools
Cost-effective for Windows-based applications
Cons:
Learning curve if transitioning from non-Microsoft environments
Limited multi-cloud capabilities
Who Should Use Azure Kubernetes?
If your organization already relies heavily on Microsoft Azure tools and services, then AKS is a seamless fit. AKS also excels for those building applications in .NET and Microsoft-friendly environments.
Kubernetes on Google Cloud: Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
Overview of Google Kubernetes
Google pioneered Kubernetes, making its Kubernetes service, Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), one of the most refined options available. GKE's strength lies in automation, ease of scaling, and a powerful developer experience.
Google Kubernetes Architecture
In GKE, the control plane is fully managed by Google, similar to the setups on AWS and Azure. GKE emphasizes automation with support for multiple operating systems, seamless upgrades, and rapid scaling—features that make it ideal for companies looking to adopt continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines.
Pros and Cons of GKE:
Pros:
Advanced automation features
Deep Kubernetes integration
Cost-effective and flexible
Cons:
Limited support for hybrid-cloud
May be complex for AWS/Azure-focused users
Who Should Use Google Kubernetes?
For tech-heavy teams focused on developer experience, GKE’s automation and ease of use make it a go-to choice. It’s ideal for companies running large-scale applications that need rapid scaling without complex management.
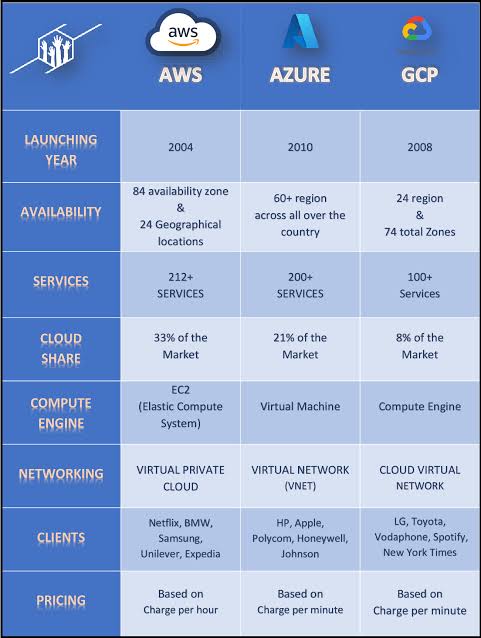
Source: Image
Steps to Start with Kubernetes
Here’s how you can get started with Kubernetes on any platform:
Create a Kubernetes Cluster: Use AWS EKS, Azure AKS, or Google GKE to launch your first cluster.
Deploy Applications: Deploy your application using the provided GUI or CLI tools.
Set Up Monitoring: Monitor your cluster’s health with tools like AWS CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, or Google Cloud Operations.
Manage Scaling: Leverage Kubernetes’ auto-scaling capabilities to handle varying workloads.
Each platform offers detailed documentation and tutorials to guide you through these steps.
These basic steps can become complex, so it’s essential to read the documentation for each provider: AWS Documentation, Azure Documentation, and Google Cloud Documentation.
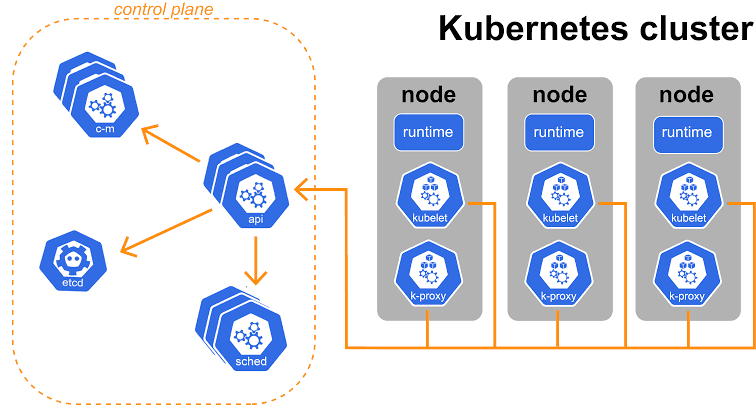
Source: Image
Choosing the Right Kubernetes Platform
Choosing between AWS, Azure, and Google Kubernetes depends largely on your existing ecosystem and project requirements.
Already using AWS for other services? EKS could save you time with its deep integration.
Microsoft-focused company? AKS offers excellent support for Windows containers.
Need developer-friendly Kubernetes with robust automation? Google Cloud’s GKE is hard to beat.
Conclusion
This Kubernetes Beginner Guide has introduced you to the fundamentals of Kubernetes and compared its deployment across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. As you embark on your Kubernetes journey, remember that each platform offers unique features tailored to different needs.
For more in-depth learning, platforms like Skillect provide beginner-friendly courses to help you gain hands-on experience and master Kubernetes in real-world scenarios.
Enroll in Skillect’s comprehensive Kubernetes course to build expertise in cloud-native technologies. Begin your journey to becoming a Kubernetes expert and unlock your potential in the world of cloud computing!
Kubernetes Beginner Guide: Comparing AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Solutions
For beginners looking to understand Kubernetes, this Kubernetes Beginner Guide provides an easy-to-follow introduction and a comprehensive comparison of how Kubernetes works across major platforms: AWS Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), and Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). Kubernetes is revolutionizing cloud computing by simplifying application deployment and scaling, and this guide is your roadmap to getting started.
Kubernetes isn’t just a buzzword—it's the backbone of modern app deployment in the cloud. Let’s say you are a DevOps engineer, a tech enthusiast, or simply someone keeping up with cloud trends. You have likely encountered Kubernetes, and for good reason. This open-source platform, originally developed by Google, has transformed how we manage containerized applications. Today, every major cloud provider, from AWS, Azure, to Google Cloud, offers a unique way to leverage Kubernetes.
Imagine Kubernetes as the 'orchestra conductor' for your applications, managing and coordinating their deployment, scalability, and maintenance. But how does it work on the big cloud platforms? And what are the core differences among AWS Kubernetes, Azure Kubernetes, and Google Kubernetes? By the end of this guide, you will not only understand these distinctions but feel confident navigating them.
What is Kubernetes?
To understand how each cloud provider manages Kubernetes, let’s start with the basics. Kubernetes is an open-source platform designed for automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. Think of it as an ecosystem where your applications can run in isolated, lightweight containers that make deployment easier and more resilient.
Kubernetes architecture revolves around a master-slave setup, with a control plane (the 'brain') and worker nodes (the 'muscles') that do the heavy lifting. This separation ensures that applications are both stable and scalable, adjusting automatically based on the demand.

Source: Image
Key Features:
Automated Rollouts: Kubernetes can automatically roll out changes without downtime.
Self-Healing: It detects failed containers and replaces them.
Service Discovery: Exposes services and their IPs to other applications.
Why Start with Kubernetes?
As cloud-native technologies dominate the tech landscape, Kubernetes has become an essential skill for developers, DevOps engineers, and IT professionals.
According to recent reports, Kubernetes usage is projected to grow by over 20% annually due to its flexibility, scalability, and support for hybrid and multi-cloud setups make it a cornerstone for modern application management. Starting with Kubernetes gives you a head start in mastering cloud computing essentials.
This guide simplifies Kubernetes concepts and focuses on comparing its deployment on AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud to help you make an informed decision.
Kubernetes on AWS: Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)
Overview of AWS Kubernetes
AWS offers the Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), an easy-to-use, fully managed service. AWS Kubernetes emphasizes scalability and integrates deeply with AWS ecosystem tools, like IAM, ELB, and CloudWatch, providing seamless authentication, monitoring, and logging.
AWS Kubernetes Architecture
The architecture on AWS typically comprises EKS clusters where each cluster holds a control plane that communicates with worker nodes. AWS handles the heavy lifting on the control plane, while users only manage the worker nodes. This split of duties makes AWS Kubernetes architecture an excellent choice for teams with limited Kubernetes experience.
Pros and Cons of EKS:
Pros:
Full integration with AWS services
Scalable and high availability
Cons:
Can be complex for beginners
Pricing can add up quickly
Who Should Use AWS Kubernetes?
AWS Kubernetes is an excellent fit for teams already invested in the AWS ecosystem or those requiring high availability and advanced scaling options.
Kubernetes on Azure: Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
Overview of Azure Kubernetes
Azure brings its Kubernetes service, known as Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), offering deep integration with its DevOps tools like Azure DevOps, GitHub Actions, and Visual Studio Code.
Azure Kubernetes Architecture
In Azure, the Kubernetes control plane and the worker nodes are separated, much like in AWS. However, Azure further simplifies deployment with automation and monitoring tools that are already popular among enterprise users. This makes AKS a preferred choice for companies running multiple applications in hybrid cloud environments.
Pros and Cons of AKS:
Pros:
Seamless integration with Microsoft tools
Cost-effective for Windows-based applications
Cons:
Learning curve if transitioning from non-Microsoft environments
Limited multi-cloud capabilities
Who Should Use Azure Kubernetes?
If your organization already relies heavily on Microsoft Azure tools and services, then AKS is a seamless fit. AKS also excels for those building applications in .NET and Microsoft-friendly environments.
Kubernetes on Google Cloud: Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
Overview of Google Kubernetes
Google pioneered Kubernetes, making its Kubernetes service, Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), one of the most refined options available. GKE's strength lies in automation, ease of scaling, and a powerful developer experience.
Google Kubernetes Architecture
In GKE, the control plane is fully managed by Google, similar to the setups on AWS and Azure. GKE emphasizes automation with support for multiple operating systems, seamless upgrades, and rapid scaling—features that make it ideal for companies looking to adopt continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines.
Pros and Cons of GKE:
Pros:
Advanced automation features
Deep Kubernetes integration
Cost-effective and flexible
Cons:
Limited support for hybrid-cloud
May be complex for AWS/Azure-focused users
Who Should Use Google Kubernetes?
For tech-heavy teams focused on developer experience, GKE’s automation and ease of use make it a go-to choice. It’s ideal for companies running large-scale applications that need rapid scaling without complex management.

Source: Image
Steps to Start with Kubernetes
Here’s how you can get started with Kubernetes on any platform:
Create a Kubernetes Cluster: Use AWS EKS, Azure AKS, or Google GKE to launch your first cluster.
Deploy Applications: Deploy your application using the provided GUI or CLI tools.
Set Up Monitoring: Monitor your cluster’s health with tools like AWS CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, or Google Cloud Operations.
Manage Scaling: Leverage Kubernetes’ auto-scaling capabilities to handle varying workloads.
Each platform offers detailed documentation and tutorials to guide you through these steps.
These basic steps can become complex, so it’s essential to read the documentation for each provider: AWS Documentation, Azure Documentation, and Google Cloud Documentation.

Source: Image
Choosing the Right Kubernetes Platform
Choosing between AWS, Azure, and Google Kubernetes depends largely on your existing ecosystem and project requirements.
Already using AWS for other services? EKS could save you time with its deep integration.
Microsoft-focused company? AKS offers excellent support for Windows containers.
Need developer-friendly Kubernetes with robust automation? Google Cloud’s GKE is hard to beat.
Conclusion
This Kubernetes Beginner Guide has introduced you to the fundamentals of Kubernetes and compared its deployment across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. As you embark on your Kubernetes journey, remember that each platform offers unique features tailored to different needs.
For more in-depth learning, platforms like Skillect provide beginner-friendly courses to help you gain hands-on experience and master Kubernetes in real-world scenarios.
Enroll in Skillect’s comprehensive Kubernetes course to build expertise in cloud-native technologies. Begin your journey to becoming a Kubernetes expert and unlock your potential in the world of cloud computing!
